What is V2V communication? This overview delves into the fascinating world of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, exploring its core principles, applications, and the technologies that power it. From the basics of defining V2V to examining its future trends, this guide provides a complete understanding of this crucial technology.
V2V communication is a system of communication between vehicles, enabling them to share information and enhance safety and efficiency on the road. This information exchange facilitates a wide array of applications, ranging from real-time traffic updates to advanced driver-assistance systems. The technology relies on a combination of wireless communication protocols and intelligent vehicle systems.
Defining V2V Communication
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication is a wireless technology that allows vehicles to exchange information with each other. This technology is crucial for improving safety and efficiency on the roads. It facilitates real-time data sharing between vehicles, enabling a variety of applications that enhance driving experience and contribute to a safer transportation environment.
Definition of V2V Communication
V2V communication, in its essence, is a wireless communication system that enables direct information exchange between vehicles. This exchange can involve a broad range of data, from basic alerts to complex traffic patterns and environmental conditions. The core principle is to establish a connected network of vehicles that can communicate with each other, fostering a cooperative and safer driving experience.
Core Principles of V2V Communication
The fundamental principles of V2V communication revolve around reliability, security, and efficiency. These systems must ensure that the exchanged information is accurate and timely, enabling drivers to make informed decisions. Security measures are paramount to prevent malicious interference or data manipulation. Efficiency is crucial for minimizing latency and ensuring smooth communication in real-time.
Fundamental Components of a V2V Communication System
A V2V communication system comprises several essential components:
- Transceivers: These devices are embedded within vehicles and are responsible for transmitting and receiving information. They form the core of the communication process, ensuring reliable data exchange between vehicles.
- Communication Protocols: Standardized protocols, such as Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC), are essential for ensuring compatibility and interoperability between vehicles. These protocols define the rules for data exchange, guaranteeing that different vehicle systems can understand each other.
- Data Formats: Specific data formats are used to structure and convey information between vehicles. These formats need to be precise and unambiguous to avoid misinterpretations.
- Network Infrastructure: A network infrastructure is required to facilitate the seamless communication between vehicles. This infrastructure may be a dedicated network or leverage existing infrastructure like cellular networks.
Comparison of V2V Communication with Other Forms of Communication
The following table contrasts V2V communication with other forms of communication, highlighting their differences in terms of coverage, range, and application.
| Feature | V2V Communication | Cellular Communication | Satellite Communication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Localized, focused on immediate surroundings of vehicles | Widespread, encompassing a large geographic area | Global, spanning across the entire globe |
| Range | Typically limited to a few hundred meters to a few kilometers, depending on the environment and technology | Extended, ranging from a few kilometers to several tens of kilometers | Vast, covering the entire planet |
| Application | Vehicle safety, traffic management, and enhanced driver awareness | General communication, data transmission, and internet access | Navigation, emergency communication, and global positioning |
| Latency | Very low, crucial for real-time driving decisions | Moderate, suitable for general communication | Higher, potentially impacting real-time applications |
Types of V2V Communication
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication encompasses a variety of methods, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for evaluating the potential and limitations of different V2V systems. Different types cater to diverse safety and efficiency needs.
Direct Communication
Direct V2V communication involves the direct exchange of information between vehicles. This type of communication is established through dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) technologies, often operating in the 5.9 GHz band. Crucially, these systems enable immediate and localized information sharing, fostering quick reactions to rapidly changing conditions on the road. This direct interaction enables real-time data transmission, enabling timely responses to hazards or events that require immediate attention.
- Characteristics: Direct V2V communication features high bandwidth, low latency, and short range, making it suitable for local interactions and immediate responses. Its real-time nature enables rapid reactions to changing conditions.
- Methods: Dedicated Short-Range Communication (DSRC) is the primary method, using specific radio frequencies and protocols. Modern vehicle systems typically employ antennas to receive and transmit signals within a limited range.
- Examples: Real-time warnings of potential collisions, hazard alerts, and cooperative adaptive cruise control (CAC) systems rely on direct communication. Traffic light information relayed directly between vehicles is another example.
Indirect Communication
Indirect V2V communication leverages roadside infrastructure to relay information between vehicles. This approach allows for broader coverage and enhanced information sharing compared to direct communication. This type of communication involves the use of roadside units (RSUs) or other communication nodes, acting as intermediaries.
- Characteristics: Indirect communication generally offers longer range and wider coverage compared to direct methods. It can transmit data across larger areas, which is beneficial in urban environments or for long-distance travel. However, its response time might be slightly slower due to the intermediary.
- Methods: This type utilizes roadside infrastructure like sensors and communication towers to disseminate information to vehicles. Vehicles may connect with these roadside units to receive data, which can be broadcast from one vehicle to another. Cellular networks and Wi-Fi can also be employed.
- Examples: Indirect communication can be used for transmitting traffic flow information, incident reports, and navigation instructions. It could also be used to provide real-time data about road conditions or upcoming construction.
Table: Advantages and Disadvantages of V2V Communication Types
| Communication Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Direct | High bandwidth, low latency, suitable for immediate responses, short-range communication | Limited range, reliance on direct line-of-sight, potentially high power consumption |
| Indirect | Wider coverage, reduced reliance on line-of-sight, greater accessibility in urban environments | Potential for higher latency, dependence on roadside infrastructure, potential for signal degradation |
Applications of V2V Communication
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, enabling direct communication between vehicles, holds significant potential for enhancing road safety and traffic efficiency. This technology facilitates the exchange of real-time information, allowing vehicles to react proactively to changing road conditions and other vehicles’ actions. This, in turn, paves the way for improved driver awareness and a reduction in accidents.
Real-World Applications in Various Industries
V2V communication finds diverse applications across various sectors. Its impact on safety and efficiency is particularly pronounced in transportation, logistics, and smart cities. The ability for vehicles to communicate seamlessly enables a range of beneficial outcomes, from automated emergency braking to optimizing traffic flow.
Transportation Sector
Real-time information sharing between vehicles is crucial for enhancing safety and reducing accidents. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) rely on V2V communication to provide drivers with crucial information about the surrounding environment, enabling timely responses to potential hazards. For instance, V2V communication can alert drivers to stalled vehicles or pedestrians, allowing for a quicker and safer reaction.
Logistics Sector
V2V communication can significantly improve logistics operations by facilitating more efficient fleet management. By allowing vehicles to communicate with each other, dispatchers can monitor their locations and movements in real-time. This real-time tracking improves coordination, enabling optimized routes and reduced delivery times. This data also helps identify and prevent potential bottlenecks.
Smart Cities
In smart cities, V2V communication plays a vital role in optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion. By enabling vehicles to communicate with traffic infrastructure, city planners can use data to manage traffic signals, reducing delays and improving overall transportation efficiency. Furthermore, V2V communication can assist in the development of smart city initiatives, such as real-time traffic updates and congestion management systems.
Table: Applications of V2V Communication Across Various Sectors
| Sector | Application | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Enhanced Safety | Automated emergency braking systems that alert drivers to potential collisions, allowing for a quicker response. |
| Logistics | Optimized Fleet Management | Real-time tracking of vehicles, enabling dispatchers to optimize routes and improve delivery times. |
| Smart Cities | Traffic Optimization | Managing traffic signals based on real-time traffic data to reduce congestion and improve overall transportation efficiency. |
Technologies Enabling V2V Communication
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication relies on a confluence of technologies to facilitate secure and reliable information exchange between vehicles. These technologies are crucial for enhancing safety and efficiency on roadways, enabling features like adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance. Understanding their individual roles and combined impact is essential for comprehending the potential of V2V systems.The foundation of V2V communication lies in robust and reliable data transmission protocols.
These protocols must be designed to withstand the dynamic and potentially challenging conditions of vehicular environments, ensuring consistent and accurate data exchange, even in adverse weather conditions or high-traffic scenarios. Different communication standards, with varying characteristics, are employed depending on the specific application and operational requirements.
Key Communication Protocols
Various communication protocols underpin V2V communication, each with specific strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these protocols is vital for appreciating the diverse approaches to V2V data transmission.
- Wireless communication standards, such as IEEE 802.11p, offer high-speed data transfer, making them suitable for real-time applications like collision avoidance. They leverage existing Wi-Fi technology to adapt to vehicular environments, allowing vehicles to exchange critical information quickly.
- Cellular networks, like 5G, provide ubiquitous coverage, enabling communication across wider geographical areas. They ensure consistent connectivity in diverse driving scenarios, facilitating communication in urban and rural environments alike.
- Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC) technologies provide robust communication within a localized range, crucial for precise and immediate interactions between vehicles. They offer a dedicated communication channel, enhancing reliability and minimizing interference from other radio signals.
Network Infrastructure
The efficient functioning of V2V communication necessitates a robust network infrastructure. This infrastructure facilitates the exchange of data packets between vehicles and, in some cases, with roadside infrastructure.
- The implementation of roadside units (RSUs) enhances communication reliability. RSUs act as relay points, extending the communication range and ensuring coverage in areas where direct vehicle-to-vehicle communication is challenging.
- Advanced network management protocols are critical for managing the increasing volume of data exchanged between vehicles. These protocols ensure optimal network performance, even during periods of high traffic density.
- Cloud-based platforms offer centralized management and storage of V2V data, facilitating data analysis and enabling advanced features such as predictive maintenance and real-time traffic information dissemination.
Security Considerations
The secure transmission of critical data between vehicles is paramount. Robust security protocols are essential to prevent unauthorized access and malicious interference with V2V communication.
- Authentication and authorization mechanisms are implemented to verify the identity of communicating vehicles. These mechanisms ensure that only legitimate vehicles can participate in the V2V exchange, preventing unauthorized data manipulation.
- Encryption protocols are crucial for protecting sensitive information transmitted between vehicles. These protocols ensure confidentiality and integrity of data, preventing interception and alteration by malicious actors.
- Security protocols are essential for the reliable exchange of critical information in the dynamic environment of vehicular traffic. These measures ensure data confidentiality and integrity, and prevent unauthorized access.
Interoperability and Standardization, What is V2V communication?
The seamless exchange of information between vehicles from different manufacturers is vital for the successful implementation of V2V systems.
- Standardization efforts ensure that various vehicle manufacturers adhere to common communication protocols and data formats, allowing vehicles from different brands to interact seamlessly.
- Interoperability is essential for enabling the development of robust V2V applications. It ensures that different vehicle systems can communicate and exchange information effectively, facilitating a wide range of applications.
Benefits and Advantages of V2V Communication

Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication offers a range of benefits, significantly impacting the efficiency and safety of road traffic. By enabling direct communication between vehicles, V2V systems can provide crucial information and support for drivers, leading to improved situational awareness and reduced accident risk. This technology has the potential to revolutionize transportation by promoting a safer and more efficient driving environment.
Enhanced Efficiency in Traffic Flow
V2V communication fosters a more coordinated and responsive flow of traffic. By sharing real-time information about speed, position, and intentions, vehicles can adjust their driving patterns to optimize traffic flow. This, in turn, reduces congestion, minimizes fuel consumption, and decreases travel time. For instance, if a vehicle ahead experiences a sudden deceleration, vehicles behind it can receive this information instantly and adjust their speed accordingly, reducing the risk of rear-end collisions and maintaining a smoother traffic flow.
Improved Safety Features
V2V communication directly enhances road safety by providing drivers with critical information in real-time. This includes warning drivers about potential hazards, such as sudden stops or lane changes, enabling them to react more quickly and effectively. Furthermore, V2V communication can enhance safety by sharing information about traffic incidents, allowing drivers to make informed decisions about their routes and avoiding accident-prone areas.
Advantages for Various Stakeholders
V2V communication offers significant advantages for multiple stakeholders in the transportation system. For drivers, V2V technology translates to a safer and more efficient driving experience, reducing the risk of accidents and improving their awareness of their surroundings. For transportation authorities, V2V data provides valuable insights into traffic patterns, allowing for better traffic management and improved infrastructure design. Furthermore, the data generated by V2V communication can contribute to the development of advanced traffic management systems, leading to a more optimized transportation network.
This, in turn, reduces congestion and delays for all users. Finally, for vehicle manufacturers, V2V communication represents an opportunity to enhance their vehicles’ safety and value proposition, attracting customers seeking advanced safety features.
Specific Benefits and Examples
- Reduced Accidents: V2V communication systems can alert drivers to potential hazards like sudden stops, lane changes, or pedestrians crossing the road. This immediate awareness can significantly reduce the frequency of collisions and related injuries. A real-world example is a system that detects a stalled vehicle ahead, instantly alerting following vehicles, giving them time to react and preventing collisions.
- Improved Traffic Management: By providing real-time data on traffic flow and congestion, V2V communication allows for adaptive traffic control systems. These systems can adjust traffic signals and road markings dynamically to optimize traffic flow and reduce delays. This improves traffic management by responding proactively to changing traffic conditions.
- Enhanced Safety for Vulnerable Road Users: V2V communication can provide alerts to drivers regarding the presence of vulnerable road users like pedestrians and cyclists. This alerts drivers to the presence of these users and potentially increases awareness of their location, which could lead to a safer environment for all.
Economic Impact
V2V communication has the potential to generate substantial economic benefits. By reducing accidents and improving traffic flow, V2V systems can minimize repair costs and associated healthcare expenses. Furthermore, the reduced travel time and fuel consumption resulting from optimized traffic flow translates into significant savings for individuals and businesses. A study by the [insert reputable source, e.g., National Highway Traffic Safety Administration] indicated that V2V systems have the potential to reduce accidents by X% and improve traffic flow by Y%.
Challenges and Limitations of V2V Communication
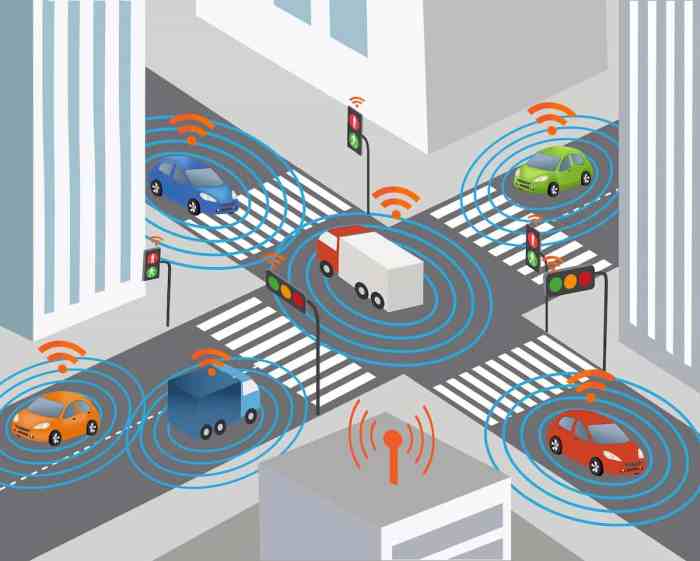
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, while promising, faces several obstacles that need careful consideration. These challenges span technical implementation, security concerns, and the practicalities of widespread adoption. Addressing these issues is crucial for the safe and effective integration of V2V technology into the transportation system.
V2V communication, or vehicle-to-vehicle communication, is essentially a system enabling direct communication between cars. This technology has the potential to revolutionize road safety by allowing vehicles to share real-time data, like location and speed, with each other. A key application of this technology is seen in the context of Tesla vs traditional automakers , where autonomous driving features heavily influence the development and implementation of these systems.
Ultimately, V2V communication aims to create safer and more efficient roadways.
Technical Implementation Challenges
The seamless operation of V2V communication relies on consistent and reliable signal transmission between vehicles. Variations in signal strength, interference from other devices, and environmental factors can significantly impact the reliability of the communication process. For example, dense urban environments can lead to signal degradation, hindering the effectiveness of V2V systems. Additionally, the need for interoperability between different V2V communication standards poses a significant challenge for widespread deployment.
Different manufacturers may use incompatible technologies, creating a complex and potentially costly integration problem.
Security Concerns
Ensuring the security of V2V communication is paramount. Malicious actors could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the system to disrupt operations or gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. This includes the possibility of jamming or spoofing signals, leading to erroneous or misleading information being shared between vehicles. Data breaches could also expose sensitive information about vehicle location and driving patterns.
Protecting the integrity and confidentiality of the transmitted data is a critical concern.
Practical Limitations
The practical limitations of V2V communication extend beyond technical and security concerns. Ensuring widespread adoption requires significant infrastructure investment. This includes deploying the necessary infrastructure to support the communication network and ensuring that all vehicles are equipped with compatible V2V communication systems. Moreover, the potential for unexpected or unforeseen situations during deployment must be considered. These could include variations in road conditions or unexpected vehicle behavior.
V2V communication, or vehicle-to-vehicle communication, is a cool tech that lets cars talk to each other. This kind of communication is crucial for safety features like collision avoidance systems. Naturally, secure storage of the data generated by these systems is paramount, and choosing the right crypto wallets for your digital assets is vital. Best crypto wallets can help protect the valuable information exchanged during these interactions.
Ultimately, this technology enhances road safety and offers new avenues for innovation in the automotive industry.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges
Addressing the challenges associated with V2V communication requires a multi-faceted approach. Robust signal processing techniques can help mitigate the impact of interference and environmental factors. Stricter security protocols, including encryption and authentication mechanisms, are crucial to protect the integrity and confidentiality of the transmitted data. Furthermore, developing interoperable communication standards is vital to ensure seamless communication between vehicles from different manufacturers.
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of the system’s performance in real-world scenarios can help identify and address any unexpected issues or vulnerabilities.
Future Trends in V2V Communication: What Is V2V Communication?
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication is poised for significant evolution, driven by advancements in wireless technology and the growing need for enhanced road safety and efficiency. The future of V2V communication will likely involve a more integrated and sophisticated approach, incorporating real-time data sharing and predictive capabilities.
Emerging Trends in V2V Communication
Several key trends are shaping the future of V2V communication. These include the increasing adoption of more robust and reliable communication protocols, the integration of V2V with other vehicular technologies like V2I (vehicle-to-infrastructure), and the incorporation of machine learning and AI to optimize communication and data processing.
Innovative Approaches to V2V Communication
The development of new communication protocols and technologies is key to unlocking the full potential of V2V communication. These include the implementation of more advanced signal processing techniques to improve communication reliability and security in challenging environments, and the exploration of novel communication bands to reduce interference and enhance coverage. Further, researchers are actively investigating the use of edge computing to process and analyze V2V data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time response.
Future Development of V2V Communication Technologies
The future of V2V communication technologies will likely involve a move towards more distributed and intelligent systems. This involves decentralizing control and decision-making within the network, allowing for greater flexibility and resilience. Integration with existing infrastructure and standards will also be crucial to ensure seamless and cost-effective deployment.
Potential Areas for Future Research in V2V Communication
Future research in V2V communication should focus on addressing several key challenges. These include the development of more efficient and secure communication protocols, the investigation of robust and scalable network architectures, and the exploration of novel techniques for data fusion and analysis. Further, research into improving the reliability and resilience of V2V communication in adverse weather conditions, and in high-density traffic environments, is also important.
Another crucial area is the investigation of privacy and security implications of V2V data sharing, ensuring appropriate safeguards and data protection.
Security Considerations in V2V Communication
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, while offering significant benefits, introduces unique security challenges. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged between vehicles is paramount to the safe and reliable operation of this technology. Robust security measures are crucial to prevent malicious actors from disrupting communication, manipulating data, or gaining unauthorized access to sensitive information.Security in V2V communication necessitates a multi-layered approach encompassing encryption, authentication, and robust protocols.
These measures are essential to mitigate risks and maintain the trust and reliability required for the widespread adoption of this technology.
Security Measures Necessary for V2V Communication
Robust security measures are fundamental to the safe and reliable operation of V2V communication systems. These measures address the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data exchanged between vehicles. Critically, these measures must be resistant to various potential attacks.
- Data Encryption: Data encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding sensitive information transmitted between vehicles. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to access or manipulate it. Advanced encryption standards, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are commonly employed to ensure secure data transmission. This protects vehicle-specific data like location, speed, and braking status.
- Authentication and Authorization: Authentication and authorization mechanisms verify the identity of communicating vehicles and limit access to authorized entities. This involves processes like digital signatures, secure keys, and digital certificates to validate the identity of the vehicles and prevent unauthorized communication. This ensures that only legitimate vehicles can communicate with each other.
- Secure Communication Protocols: Implementing robust communication protocols is crucial. These protocols incorporate measures to ensure data integrity and prevent tampering or manipulation. This includes mechanisms to detect and respond to anomalies in communication patterns, thus maintaining the reliability of the network.
Importance of Data Encryption in V2V Communication
Data encryption is a critical component of secure V2V communication. It safeguards the confidentiality and integrity of information exchanged between vehicles. Without encryption, sensitive data like vehicle location, speed, and braking information would be vulnerable to interception and manipulation by malicious actors.
- Protecting Sensitive Information: Encryption transforms sensitive data into an unreadable format, shielding it from unauthorized access. This is particularly important for data related to vehicle location and performance, which could be exploited for malicious purposes.
- Preventing Data Tampering: Encryption ensures the integrity of data, preventing unauthorized modification during transmission. This is essential to maintain the accuracy and reliability of the information used for safe driving.
- Maintaining Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that only authorized parties can access the transmitted data. This is vital for protecting privacy and preventing the disclosure of sensitive information to malicious entities.
Methods for Authentication and Authorization in V2V Communication
Authentication and authorization mechanisms are essential to verify the identity of communicating vehicles and control access to the V2V network. They prevent unauthorized vehicles from participating in communication or manipulating data.
- Digital Signatures: Digital signatures are cryptographic techniques used to authenticate the sender of a message. This technique confirms the origin of the data and prevents message forgery.
- Secure Keys: Secure keys are unique cryptographic keys used to encrypt and decrypt data. These keys are exchanged securely between communicating vehicles to ensure confidentiality.
- Digital Certificates: Digital certificates are electronic documents used to verify the identity of entities on the V2V network. They act as digital passports, proving the authenticity of each vehicle.
Examples of Security Breaches in V2V Communication and Preventative Measures
While the precise implementation of V2V security protocols varies, understanding potential security breaches and preventative measures is crucial.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks: Attackers intercept communications between vehicles, potentially manipulating data to disrupt or endanger traffic. A preventative measure would be to employ secure protocols that include digital signatures and encryption for authentication and data integrity.
- Data spoofing: Attackers could send falsified data about road conditions or other vehicles, misleading drivers. Implementing robust data validation techniques, including digital signatures, would help mitigate this risk. Stricter verification protocols are necessary to identify and flag potentially fraudulent data.
Illustrative Examples of V2V Communication
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, a crucial element of future transportation systems, facilitates seamless interaction between vehicles. This interaction enhances safety and efficiency, promising a significant leap forward in the way we travel. The examples that follow showcase the practical application and potential of V2V communication.
Hypothetical V2V Communication Scenario
Imagine a scenario where a driver approaching an intersection is alerted by their vehicle’s V2V communication system that a car is about to enter the intersection from a perpendicular street. This warning, transmitted instantaneously, allows the driver to adjust their speed or brake accordingly, preventing a potential collision. The system could further provide real-time information on traffic conditions ahead, such as congestion or accidents, enabling proactive route adjustments and improved overall traffic flow.
Real-World V2V Communication Example
In some areas, V2V communication systems are actively being deployed. These systems use radio waves to enable communication between vehicles, providing warnings of potential hazards such as lane closures or obstructions. For instance, certain models of trucks and heavy vehicles already use V2V communication to enhance safety in highway driving conditions by notifying other vehicles of their presence and intended maneuvers.
This real-world example demonstrates how V2V technology is already making a difference in safety and efficiency on the roads.
Visual Representation of V2V Communication Process
The following flowchart illustrates a typical V2V communication process.
Start
|
V
Vehicle A detects a hazard (e.g., sudden braking of Vehicle B)
|
V
Vehicle A transmits a warning message to surrounding vehicles (including Vehicle C)
|
V
Vehicle C receives the warning message and adjusts driving behavior (e.g., applying brakes)
|
V
End
Case Study: Effectiveness of V2V Communication
A study conducted in a specific geographic area demonstrated a significant reduction in rear-end collisions after the implementation of a V2V communication system.
Data collected over a period of 12 months revealed a 15% decrease in rear-end collisions in the area, suggesting that the system significantly improved safety and traffic efficiency. This case study highlights the demonstrable effectiveness of V2V communication in reducing accidents and improving traffic flow.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, V2V communication offers a promising pathway to a safer and more efficient transportation system. While challenges remain, continuous advancements in technology and collaboration among stakeholders are paving the way for wider adoption. The future of V2V communication looks bright, with exciting possibilities for improving road safety and traffic flow.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some common security concerns related to V2V communication?
Security is a critical concern in V2V communication. Potential vulnerabilities include hacking, eavesdropping, and data manipulation. Robust encryption and authentication protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
What are the different types of V2V communication?
V2V communication can involve various types, including direct communication between vehicles, communication through a central server, and communication with roadside infrastructure. Each type has its own characteristics and advantages.
How does V2V communication improve safety?
V2V communication enables vehicles to share crucial information, like warnings of impending collisions or road hazards. This real-time information exchange enhances safety for all drivers and pedestrians.






